In today’s complex and fast-paced business environment, understanding compliance regulations is essential. Whether you’re a small startup or a large enterprise, staying compliant with evolving laws and regulations is not only about avoiding penalties, it’s about building trust, protecting data, and operating with integrity.
Compliance regulations are legal requirements established by regulatory bodies and federal agencies to govern how organizations manage risk, protect consumers, handle data, and maintain ethical business practices. From data privacy laws to financial reporting standards, these regulations span across every industry and region, making regulatory compliance a foundational element of modern business operations.
Why Regulatory Compliance Matters
Regulatory compliance ensures that an organization’s business operations align with applicable legal standards, ethical principles, and industry-specific regulations. These requirements help prevent non-compliance, which can result in severe consequences including financial penalties, legal liabilities, damaged reputation, or even criminal prosecution.
When compliance is prioritized, businesses are more likely to earn the trust of consumers, regulators, investors, and stakeholders, while also avoiding risks associated with regulatory violations or compliance failures.
The Role of Compliance in Business Operations
Compliance regulations directly impact a wide range of business processes, from how customer data is collected and stored, to how financial reports are prepared, to how employees are trained and monitored. Embedding regulatory compliance into daily business operations creates a culture of accountability, reduces business risk, and supports long-term operational efficiency.
Organizations that proactively integrate compliance programs into their strategic objectives are more agile and resilient in the face of regulatory change.
Key Laws and Regulatory Frameworks
Several major regulations and frameworks define today’s compliance landscape:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): A European Union regulation that protects the personal data of individuals and governs how organizations collect, process, and store sensitive information.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): Grants California residents specific rights regarding their consumer data, including the right to opt-out of data sales and request data deletion.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): Enforces data protection and privacy standards in the healthcare sector, ensuring the confidentiality of sensitive health information.
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX): A U.S. law requiring public companies to maintain accurate financial reporting, implement internal controls, and ensure transparency in financial disclosures.
Elements of a Strong Compliance Program
To maintain regulatory compliance, businesses must develop comprehensive compliance programs that include:
- Documented internal policies aligned with applicable laws and industry standards
- A designated compliance officer or Chief Compliance Officer (CCO) responsible for oversight
- Regular compliance audits and risk assessments
- Clear compliance controls and protocols to address vulnerabilities
- Ongoing employee training to identify and prevent unethical or illegal practices

These elements work together to identify and address compliance risks, support consistent compliance monitoring, and ensure a business remains compliant across departments and functions.
The Impact of Industry-Specific Compliance Regulations
Each industry faces unique compliance requirements. For example:
- Financial institutions must follow financial compliance laws such as SOX and adhere to anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) rules.
- Healthcare organizations are required to implement compliance policies under HIPAA to protect patient data and ensure data security.
- E-commerce companies and technology providers must maintain data privacy standards under laws like GDPR and CCPA to safeguard consumer data and prevent data breaches.
Understanding these industry-specific regulations is essential for tailoring compliance efforts to meet both regulatory and operational needs.
Non-Compliance: What Happens When Regulations Are Ignored
Non-compliance can result in far-reaching consequences for organizations. These include:
- Expensive regulatory fines
- Legal investigations and lawsuits
- Revocation of business licenses or certifications
- Erosion of consumer and investor trust
- Operational disruptions and reputational harm
Maintaining compliance standards isn’t just about risk mitigation, it’s about business continuity, brand protection, and stakeholder confidence.
How Compliance Software Supports Regulatory Compliance
In a digital-first business world, many organizations are adopting compliance software to simplify and automate their compliance management processes. These platforms help businesses:
- Centralize and secure electronic documents
- Automate compliance monitoring and alerts
- Track and enforce internal policies and compliance controls
- Manage risk assessments and audit preparation
- Streamline training programs for employees
By leveraging compliance management tools, companies reduce manual tasks, improve accuracy, and maintain better oversight of evolving regulatory requirements.
The Role of a Compliance Officer
A compliance officer is responsible for implementing, monitoring, and refining an organization’s compliance program. Their duties may include:
- Ensuring the company adheres to relevant laws
- Conducting internal compliance audits
- Investigating and resolving compliance violations
- Preparing for external audits by regulatory agencies
- Keeping up with changes to regulatory compliance requirements
For many companies, hiring a Chief Compliance Officer (CCO) is a strategic investment that brings credibility and structure to their regulatory compliance efforts.
Training and Awareness in Regulatory Compliance
No compliance policy can succeed without buy-in from employees. Comprehensive compliance training ensures that:
- Employees understand relevant regulations and industry standards
- Ethical conduct becomes a norm across all departments
- Employees can identify potential compliance risks or red flags
- Teams are equipped to respond to evolving compliance challenges
Ongoing education is key to maintaining a compliance culture within your organization.
Maintaining Compliance Through Continuous Monitoring
Compliance is not a one-time event, it’s an ongoing process. Continuous compliance monitoring involves:
- Tracking changes to relevant laws and regulatory requirements
- Auditing business practices and compliance data
- Reviewing and updating compliance policies
- Responding quickly to data breaches or incidents
- Ensuring compliance controls remain effective
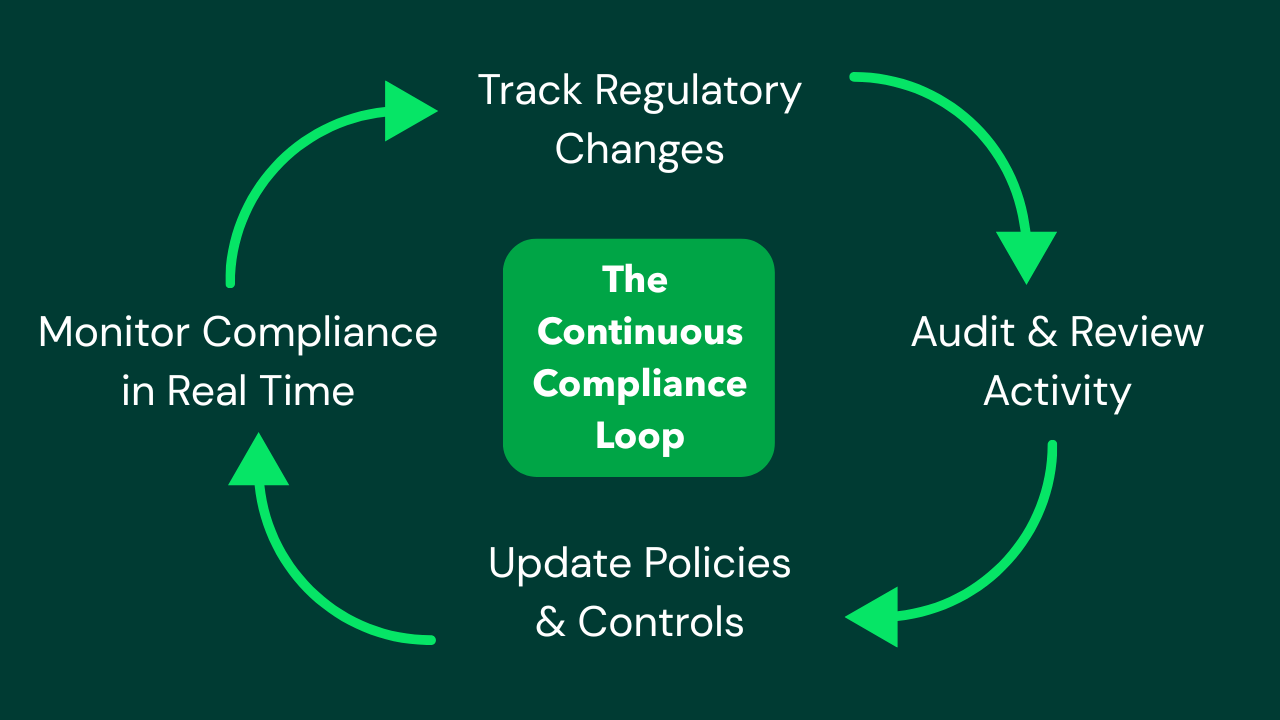
This proactive approach helps businesses avoid surprises and stay ahead of regulatory demands.
Best Practices for Compliance Documentation
Accurate documentation supports your ability to demonstrate compliance during inspections or audits. Your records should include:
- Versions of compliance policies and procedures
- Employee training completion reports
- Records of compliance tasks, incident reports, and audits
- Documentation of data protection protocols
- Logs from compliance monitoring systems
Well-organized documentation also supports internal reviews and improves regulatory readiness.
Building a Culture of Compliance
True compliance starts at the top. When leadership embraces regulatory compliance as a strategic priority, it sets the tone for the entire organization. A robust compliance program is most effective when compliance is part of your business DNA, not an afterthought.
By embedding compliance controls, reinforcing expectations through training, and recognizing compliance achievements, organizations can create a proactive, compliance-first culture.
The Future of Regulatory Compliance
As regulations evolve and enforcement becomes more stringent, businesses must stay agile. Expect to see increased focus on:
- Consumer data protection
- AI governance and compliance
- Cross-border regulatory harmonization
- ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) compliance standards
- Expansion of cybersecurity frameworks like NIST
Adapting your compliance program to these new frontiers will be critical for sustainable success.
Final Thoughts
Compliance regulations protect businesses, consumers, and society at large. Whether you’re navigating regulations or another compliance requirement, the stakes have never been higher. Skematic helps organizations take a proactive approach by making compliance operations more transparent, structured, and reliable.
Establishing a structured, scalable, and well-documented compliance management system is one of the most important steps a business can take today. By doing so, you not only stay ahead of regulatory changes, but also build a brand that is trusted, ethical, and resilient. With Skematic, firms can move away from scattered tools and toward one unified platform designed for modern compliance needs.
If you’re looking for a smarter way to manage compliance risks, streamline compliance tasks, and stay aligned with compliance standards, now is the time to act.
Want help with your compliance strategy?
Explore how a modern compliance management solution like Skematic can automate monitoring, enhance visibility, and simplify reporting, while ensuring your organization stays ahead of today’s regulatory landscape.
Let’s build a future where your business doesn’t just meet compliance regulations.Request a Demo



